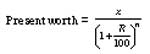(Study Materials) Numerical Ability/Quantitative Aptitude : Simple & Compound Interest
(Study Materials) Numerical Ability/Quantitative Aptitude : Simple & Compound Interest
Simple Interest
It is the sum which is paid by the borrower to the lender for using the money
for a specific time period. The money borrowed is called the Principal. The rate
at which the interest is calculated on the principal is called Rate of Interest.
The time for which the money is borrowed is Time and the total sum of principal
and interest is called the Amount.
Simple Interest
If P = Principal, R = Rate per cent per annum T = Number of years, SI = Simple Interest and A = Amount. Then,
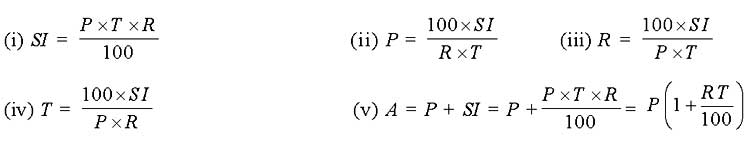
Here, the interest is calculated on the original principal ie, the principal to calculate the interest remains constant throughout the time period. The interest earned on the principal is not taken into account for the purpose of calculating interest for later years.
Compound Interest
In compound interest, the interest is added to the principal at the end of each period and the amount thus obtained becomes the principal for the next period. The process is repeated till the end of the specified time.
If P = Principal,
R = Rate per cent per annum
Time = Number of years,
CI = Compound Interest
A = Amount. Then,
When the interest is compounded annually
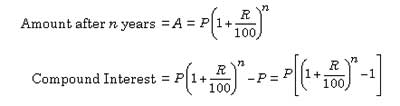
Important Formulae
1. If the rate of interest differs from year to year ie, R1 in the first year, R2 in the second year, R3 in the third year.
Then
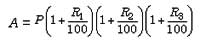
2. When the principal changes every year, we say that the interest is compounded annually. Then,
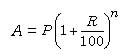
3. When the principal changes as per every six months, we say that the interest is compounded half yearly or semi-annually. Then,
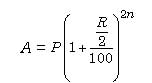
4. When the principal changes every three months, we say that the interest is compounded quarterly. Then,
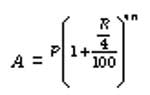
5. When the principal changes after every month, we say that the interest is compounded monthly. Then,
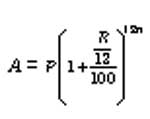
6. When the interest is compounded annually but time is in fraction say year.
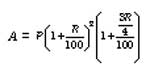
7. The difference between the simple interest and compound interest for 2 year (or terms) is given by the formula
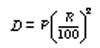
Where D is the difference, P is the principal and R is the rate of interest.
8. Present worth of x ` due n years, hence is given by