
Study Materials for IBPS, Bank Exams : Numerical
Ability/Quantitative Aptitude - Number System
Place Value (Indian)
Face Value and Place Value of a Digit
Face Value: It is the value of the digit itself eg, in 3452, face
value of 4 is ‘four’, face value of 2 is ‘two’.
Place Value: It is the face value of the digit multiplied by the place
value at which it is situated eg, in 2586, place value of 5 is 5 × 102 = 500.
Number Categories
Natural Numbers (N): If N is the set of natural numbers, then we write N =
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6,…}
The smallest natural number is 1.
Whole Numbers (W): If W is the set of whole numbers, then we write W = {0, 1, 2,
3, 4, 5,…}
The smallest whole number is 0.
Integers (I): If I is the set of integers, then we write I = {– 3, –2, –1, 0,
1, 2, 3, …}
Rational Numbers: Any number which can be expressed in the form of p/q, where p
and q are both integers and q # 0 are called rational numbers.
e.g. 3/2,7/9,5,2
There exists infinite number of rational numbers between any two rational
numbers. Irrational Numbers Non-recurring and non-terminating decimals are
called irrational numbers. These numbers cannot be expressed in the form of p/q
.
e.g. √3, √5,√29
Real Numbers: Real number includes both rational
and irrational numbers.
Basic Rules on Natural Numbers
1. One digit numbers are from 1 to 9. There are 9 one digit numbers. ie, 9 ×
100.
2. Two digit numbers are from 10 to 99. There, are 90 two digit numbers. ie, 9 ×
10.
3. Three digit numbers are from 100 to 199. There are 900 three digit numbers ie,
9 × 102.
In general the number of n digit numbers are 9 × 10(n–1)
Sum of the first n, natural numbers ie, 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + … + n = n n 1 / 2
Sum of the squares of the first n natural numbers ie. 12 + 23
+ 32 + 42 + …+ n2 = n n 1 2n 1 / 6
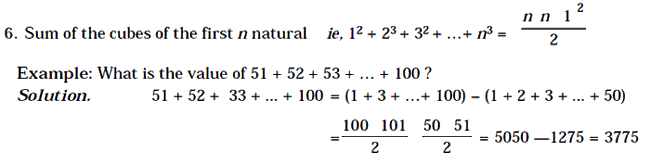
Different Types of Numbers
Even Numbers: Numbers which are exactly divisible by 2 are called even
numbers.
eg, – 4, – 2, 0, 2, 4…
Sum of first n even numbers = n (n + 1)
Odd Numbers: Numbers which are not exactly divisible by 2 are called odd
numbers.
eg, – 5, –3, –1, 0, 1, 3, 5…
Sum of first n odd numbers = n2
Prime Numbers: Numbers which are divisible by one and itself only are called
prime numbers.
eg, 2, 3, 5, 7, 11…
- 2 is the only even prime number.
- 1 is not a prime number because it has two equal factors.
- Every prime number greater than 3 can be written in the form of (6K + 1)
or (6K – 1) where K is an integer.
- There are 15 prime numbers between 1 and 50 and l0 prime numbers between
50 and 100.