(Papers) IBPS Clerk Previous Year Exam Paper "Held on 04-12-2011, 1st Sitting - Reasoning" (Eastern Zone)
1. In a certain code GRANT is written as UOBSH and PRIDE is written as FEJSQ. How is SOLD written in that code?
(1) EPMT
(2) TPME
(3) EMPT
(4) CKNR
(5) ETPM
2. Four of the following five are alike in a certain way and so form a group. Which is the one that does not belong to that group?
(1) 19
(2) 17
(3) 13
(4) 27
(5) 37
3. How many meaningful English words can be made with the second, the fourth, the sixth and the seventh letters of the word STUMBLE using each letter only once in each word?
(1) None
(2) One
(3) Two
(4) Three
(5) More than three
4. What should come in place of the question mark (?) in the following letter series based on the English alphabetical order?
BE GJ LO QT ?
(1) UX
(2) VY
(3) SV
(4) RU
(5) WZ
5. How many such pairs of letters are there in the word GOVERNMENT each of which has as many letters between them in the word (in both forward and backward directions) as in the English alphabet?
(1) None
(2) One
(3) Two
(4) Three
(5) More than three
Directions (6-10): In the following questions, the symbols d %, $, # and @ are used with the following meaning as illustrated below:
‘P $ Q’ means ‘P is not smaller than Q’.
‘P @ Q’ means ‘P is not greater than Q’.
‘P d Q’ means ‘P is neither smaller than nor equal to Q’.
‘P # Q’ means ‘P is neither greater than nor equal to Q’.
‘P % Q’ means ‘P is neither smaller than nor greater than Q’.
Now in each of the following questions assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the two conclusions I and II given below them is/are definitely true?
Give answer (1) if only Conclusion I is true.
Give answer (2) if only Conclusion II is true.
Give answer (3) if either Conclusion I or II is true.
Give answer (4) if neither Conclusion I nor II is true.
Give answer (5) if both Conclusions I and II are true.

6. Statements :
F @ N, N R. H @ R
Conclusions:
I. H d N
II. F # R
7. Statements :
M # T, T @ K. K $ N
Conclusions:
I. M # N
II. K d M
8. Statements :
T%H, H$W
Conclusions:
I. W # T
II. W % T
9. Statements :
N d K. K # D, D % M
Conclusions:
I. M d K
II. D d N
10. Statements:
J $ B, B % R. R d F
Conclusions:
I. F # B
II. R @ J
Directions (11-15): Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
A, B, C, D, E, F and G are Sitting around a circle facing the centre, not necessarily in the same order. D is not second to the left of F but D is second to the right of A. C. is third to the right of A and C is second to the left of G. B is not an immediate neighbour of G.
11. Who is to the immediate right of C?
(1) D
(2) G
(3) E
(4) B
(5) Data inadequate
12. Who is the only one person sitting between A and G?
(1) B
(2) D
(3) C
(4) E
(5) F
13. Who is to the immediate left of D?
(1) B
(2) C
(3) A
(4) Data inadequate
(5) None of these
14. Who is second to the left of C?
(1) B
(2) G
(3) F
(4) Data inadequate
(5) None of these
15. What is E’s position with respect to D?
(1) To the immediate right
(2) To the immediate left
(3) Third to the right
(4) Second to the right
(5) Third to the left
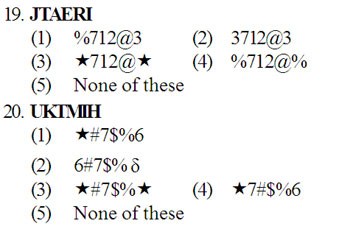
Directions (16-20): In each question below is given a group of letters followed by four combinations of digits/symbols numbered (1), (2), (3) and (4). You have to find out which of the combinations correctly represents the group of letters based on the coding system and the conditions given below and mark the number of that combination as ;your answer. If none of the carbonations correctly represents the group of letters, mark (5) i.e. ‘None of these’ as your answer.
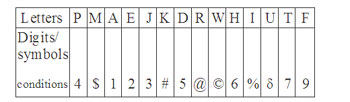
(i) If the first letter is a consonant and the last letter is a vowel, the codes of both these are to be interchanged.
(ii) If both the first and the last letters are consonants both these are to be coded as per the code of the last letter.
(iii) If the first letter is vowel and the last letter is a consonant both these are to be coded as ‘*’.
Note: All the remaining letters are to be coded as per their original codes.
16. ERWHKA
(1) 2@©6#1
(2) 1@©6#2
(3) 1@©6#1
(4) 2@©6#2
(5) None of these
17. MPEKDU
(1) $42#5
(2) $42#5$
(3) d42#5
(4) d425#$
(5) None of these
18. TMEIUF
(1) 7$2%d9
(2) 7$2%d7
(3) 9$2%d7
(4) 9$2%d9
(5) None of these
Directions (21-25): Each of the questions below consists of a question and two statements numbered I and II given below it. You have to decide whether the data provided in the statements are sufficient to answer the question. Read both the statements and—
Give answer (1) if the data in statement I alone are sufficient to answer the question, while the data in statement II alone are not sufficient to answer the question.
Give answer (2) if the data in statement II alone are sufficient to answer the question, while the data in statement I alone are not sufficient to answer the question.
Give answer (3) if the data either in statement I alone or in statement II alone are sufficient to answer the question.
Give answer (4) if the data given in both the statements I and II together are not sufficient to answer the question.
Give answer (5) if the data in both the statements I and II together are necessary to answer the question.
21. In a row of girls facing North, what is D’s position from the left end?
I. D is twentieth from the right end.
II. There are ten girls between B and D.
22. Town M is towards which direction of Town K?
I. Town K is towards North- West of Town D.
II. Town M is towards South-East of Town D.
23. How many daughters does P have?
I. K and M are sisters of T.
II. T’s father is husband of P’s mother.
24. On which day of the week from Monday to Sunday did Arun leave for London?
I. Arun did not leave for London during the weekend.
II. Arun’s brother left for London on Friday two days after Arun left for London.
25. How is ‘new’ written in a code language?
I. ‘new good clothes’ is written as ‘5 3 9’ in that code language.
II. ‘good clothes are costly’ is written as ‘ 9 6 7 3’ in that code language.
Directions (26-30): Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions:
A word and number arrangement machine when given an input line of words and numbers rearranges them following a particular rule in each step. The following is an illustration of input and rearrangement, (All numbers are two-digit numbers.) Input : good for everything 19 37 26 all 65
Step I : all good for everything 19 37 26 65
Step II : all 65 good for everything 1937 26
Step III : all 65 everything good for 19 37 26
Step IV : all 65 everything 37 good for 19 26
Step V : all 65 everything 37 for good 19 26
Step VI : all 65 everything 37 for 26 good 19
and Step VI is the last step of the rearrangement as the desired arrangement is reached. As per the rules followed in the above steps, find out in each of the following questions the appropriate step for the given input. (All numbers are two-digit numbers.)
26. Input: won 13 now 25 72 please go 47
How many steps will be required to complete the rearrangement ?
(1) Four
(2) Five
(3) Six
(4) Three
(5) None of these
27. Step III of an input is :
car 81 desk 15 42 39 tall more
Which of the following will be Step VI?
(1) car 81 desk 42 39 15 tall more
(2) car 81 desk 42 15 39 tall more
(3) car 81 desk 42 more 39 15 tall
(4) There will be no such step.
(5) None of these
28. Step II of an input is :
bell 53 town hall near 27 43 12
How many more steps will be required to complete the rearrangement?
(1) Five
(2) Four
(3) Six
(4) Three
(5) None of these
29. Step II of an input is :
box 93 25 year end 41 32 value
Which of the following is def tmtely the input?
(1) 25 year end box 93 41 32 value
(2) 25 year end 93 41 32 value box
(3) 9325 box year end 41 32 value
(4) Cannot be determined
(5) None of these
30. Input:
paper dry 37 23 height call 62 51
Which of the following steps will be the last but one?
(1) V
(2) IV
(3) VI
(4) III
(5) None of these
Directions (31-35): Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
P, Q, R. S, T, V and W are travelling in three buses A, B and C with at least two of them in any of these buses.
Each of them has a favourite (likes) cuisine viz. Punjabi, Rajasthani, Bengali, Maharashtrian, Gujarati. Kashmirt and Udipi not necessarily in the same order.
Q is travelling in bus B with T. T’s favourtte cuisine is Udtpi. Those who travel in bus A do not like Punjabi and Maharashtrian cuisines. The one who likes Rajasthani cuisine travels only with W in bus C. The one whose favourite cuisine is Gujarati does not travel in the same bus with either T or W. P does not travel in bus B. P likes Kashmiri cuisine. S and V are travelling in the same bus. V does not like Bengali cuisine. The one whose favourite cuisine is Maharashtrian does not travel in Bus B.
31. Which of the following combinations is correct?
(1) A-V-Gujarati
(2) B-S-Bengali
(3) C-W-Punjabi
(4) B-Q-Gujarati
(5) All are incorrect
32. Whose favourite cuisine is Rajasthani?
(1) Q
(2) S
(3) V
(4) R
(5) Data inadequate
33. What is S’s favourite cuisine?
(1) Maharashtrian
(2) Bengali
(3) Rajasthani
(4) Kashmiri
(5) Data inadequate
34. What is Q’s favourite cuisine?
(1) Kashmiri
(2) Maharashtrian
(3) Punjabi
(4) Data inadequate
(5) None of these
35. In which bus are three of them travelling?
(1) A only
(2) B only
(3) A or B only
(4) Data inadequate
(5) None of these
Directions (36-40) : In each question below are two statements followed by two conclusions numbered I and II. You have to take the two given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Give answer (1) if only conclusion I follows.
Give answer (2) if only conclusion II follows.
Give answer (3) if either conclusion I or II follows.
Give answer (4) if neither conclusion I nor II follows.
Give answer (5) if both conclusions I and II follow.
36. Statements :
No holiday is vacations.
Some vacations are trips,
Conclusions:
I. No trip is a holiday,
II. Some holidays are definitely not trips.
37. Statements :
Some kites are birds,
No kite is an aeroplane.
Conclusions:
I. All aeroplanes are birds.
II. Some birds are definitely not kites.
38. Statements :
All metals are plastics.
All plastics are fibres.
Conclusions:
I. Atleast some fibres are metals.
II. Some metals are not fibres.
39. Statements :
All roads are streets.
No street is a highway.
Conclusions:
I. No highway is a road.
II. All streets are roads.
40. Statements :
Some animals are plants.
All plants are rocks.
Conclusions:
I. All plants are animals.
II. Atleast some rocks are animals.
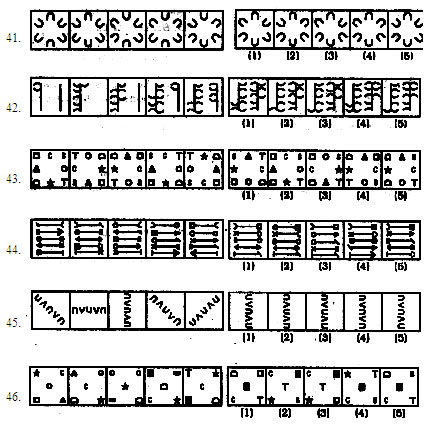
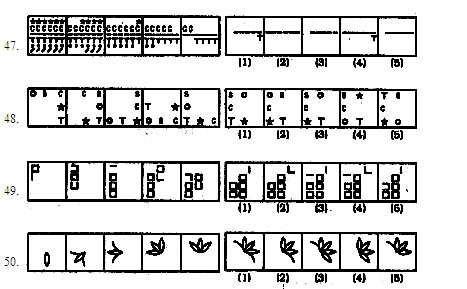
Directions (41-50) : In each of the questions given below which one of the five answer figures on the right should come after the problem figures on the left, if the sequence were continued?